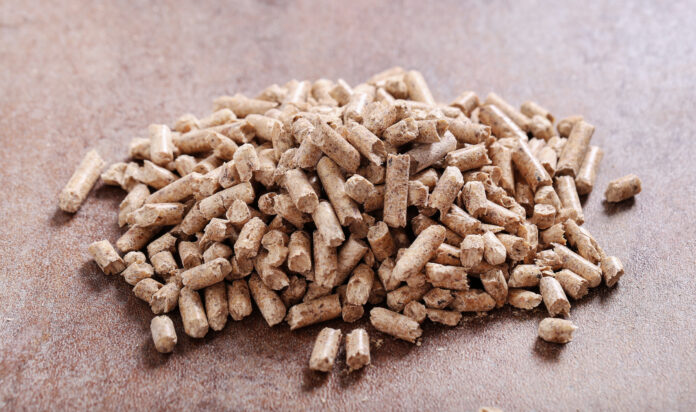
Mipa Overseas Distribute High Quality ofCattle feed which refers to the total diet provided to cattle to meet their nutritional requirements for growth, maintenance, reproduction, and production. It encompasses a combination of different ingredients and supplements designed to provide the necessary nutrients for the health and well-being of the animals. Our Cattle feed typically consists of:
- Forages: Including pasture grasses, legumes, and harvested forages such as hay and silage. Forages provide fiber, energy, protein, vitamins, and minerals essential for cattle health and productivity.
- Concentrates: These are energy-rich feeds that provide additional calories and protein to the diet. Common concentrates include grains like corn, barley, oats, and protein sources like soybean meal and distillers grains.
- Minerals and Vitamins: Mineral supplements provide essential minerals such as calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, potassium, and trace minerals. Vitamin supplements provide vitamins such as A, D, E, and various B vitamins that may be lacking in the diet.
- Protein Supplements: These supplements are fed to ensure adequate protein intake, especially when forages are low in protein or of poor quality. Common protein supplements include soybean meal, cottonseed meal, and distillers grains.
- Additives and Medications: These are substances added to the feed to improve feed efficiency, promote growth, enhance digestion, prevent disease, or treat specific health conditions. Examples include antibiotics, probiotics, enzymes, antioxidants, ionophores, and parasiticides.
Our Cattle feed is formulated based on factors such as cattle breed, age, production stage, nutritional requirements, available resources, and management objectives. It’s essential for producers to work with nutritionists, veterinarians, and extension specialists to develop balanced and cost-effective feeding programs tailored to their specific herd and production goals.
Cattle Feed Composition ?
- Protein Sources:
- Soybean Meal: One of the most widely used protein sources in cattle feed. Soybean meal is rich in essential amino acids and is highly digestible for cattle.
- Corn Gluten Meal: A byproduct of corn processing, corn gluten meal is rich in protein and often used as a protein supplement in cattle feed.
- Distillers Grains: Byproducts of the ethanol production process, distillers grains are rich in protein and energy, making them a valuable feed ingredient for cattle.
- Cottonseed Meal: A byproduct of the cotton industry, cottonseed meal is a good source of protein for cattle feed. However, it should be used with caution due to its high levels of gossypol, which can be toxic to some animals in high concentrations.
- Canola Meal: Canola meal is a byproduct of the oil extraction process from canola seeds. It is a good source of protein and often used in cattle feed.
- Sunflower Meal: Similar to soybean meal, sunflower meal is derived from the oil extraction process of sunflower seeds. It is rich in protein and commonly used in cattle feed.
- Energy Sources:
- Grains: Grains like corn (maize), barley, oats, and sorghum are commonly used in cattle feed. They are rich in carbohydrates, providing energy to the animals.
- Oilseeds: Oilseeds such as soybeans, sunflower seeds, and cottonseeds are valuable components of cattle feed. They are high in fat, which serves as a concentrated energy source.
- Forage: Forage crops like alfalfa, clover, and grasses are essential for providing fiber in the cattle diet. While they are not as energy-dense as grains and oilseeds, forages contribute to the overall energy balance and support the digestive health of cattle.
- Vitamins:
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Vitamin K
- B vitamins (thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, etc.)
- Minerals:
- Calcium
- Phosphorus
- Magnesium
- Potassium
- Sodium
- Chloride
- Sulfur
- Trace minerals (iron, zinc, copper, manganese, selenium, iodine)
- Salt: Sodium chloride is often added to cattle feed to meet sodium and chloride requirements and to enhance palatability.
- Microbial Supplements: Probiotics and yeast cultures are sometimes included to support digestive health and improve feed efficiency.
- Antioxidants: Substances like vitamin E or selenium may be added to prevent the oxidation of fats and maintain feed quality.
- Growth Promoters: Some feed additives, such as ionophores or antibiotics, may be used to improve feed efficiency and promote growth in cattle. However, regulations regarding the use of these additives vary by region and may require veterinary oversight or prescription.
- Rumen Buffers: Ingredients like sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) or magnesium oxide are added to help stabilize rumen pH and prevent acidosis.
- Mycotoxin Binders: These additives are included to mitigate the negative effects of mycotoxins, which can be present in feed ingredients contaminated by molds.