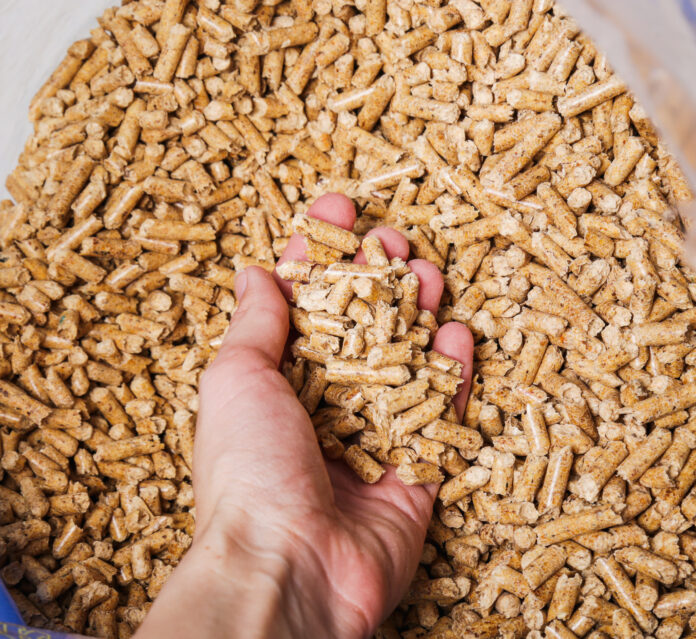
Broiler layer feed is specifically formulated to meet the nutritional requirements of laying hens (also known as layers) to support egg production and overall health. Unlike broilers, which are raised for meat production, layers are raised primarily for egg production. The feed composition and nutrient levels in broiler layer feed are tailored to meet the unique needs of laying hens throughout various stages of egg production. Here’s an overview of broiler layer feed:
- Feed Form: Broiler layer feed can be provided in various forms, including pellets, crumbles, or mash, similar to broiler finisher feed. The choice of feed form may depend on factors such as flock age, management practices, and feeding equipment.
- Nutrient Composition: Broiler layer feed typically contains a balanced combination of essential nutrients to support egg production, shell quality, and overall bird health. Key components of broiler layer feed include:
- Protein: Laying hens require a higher level of protein in their diet compared to broilers to support egg production. The protein content in broiler layer feed is typically around 16-18%, with amino acids such as methionine and lysine being particularly important for optimal egg production.
- Calcium and Phosphorus: Adequate levels of calcium and phosphorus are essential for shell formation and skeletal health in laying hens. Broiler layer feed contains higher levels of calcium (around 3.5-4%) compared to broiler feed to support eggshell quality.
- Energy: Laying hens require sufficient energy to support egg production and maintenance functions. Energy sources such as grains, fats, and oils are included in broiler layer feed to meet these requirements.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Broiler layer feed contains a comprehensive blend of vitamins and minerals to support overall health, reproductive performance, and immune function. This may include vitamins A, D, E, B-complex vitamins, and minerals such as selenium, zinc, and manganese.
- Additives: Some broiler layer feeds may contain additives such as probiotics, prebiotics, enzymes, or organic acids to promote gut health, nutrient utilization, and overall performance in laying hens.
- Phase Feeding: Similar to broilers, layer feed may be provided in different phases based on the age and production stage of the flock. Starter, grower, developer, and layer feeds are commonly used to meet the changing nutritional needs of laying hens throughout their production cycle.
Broiler Grower Composition ?
- Protein: Laying hens require a higher level of protein in their diet compared to broilers to support egg production. The protein content in broiler layer feed typically ranges from 16% to 18%. High-quality protein sources such as soybean meal, canola meal, and fish meal are commonly used to provide essential amino acids necessary for egg production and muscle maintenance.
- Calcium and Phosphorus: Adequate levels of calcium and phosphorus are essential for shell formation, skeletal health, and eggshell quality in laying hens. Broiler layer feed contains higher levels of calcium (around 3.5% to 4%) compared to broiler feed to support these requirements. Phosphorus levels are also adjusted to maintain the proper calcium-to-phosphorus ratio for optimal eggshell quality and bone health.
- Energy: Laying hens require sufficient energy to support egg production, maintenance functions, and body temperature regulation. Energy sources such as grains (e.g., corn, wheat), fats, and oils are included in broiler layer feed to meet these requirements. The energy content of layer feed is carefully balanced to support high levels of egg production without excessive body fat deposition.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Broiler layer feed contains a comprehensive blend of vitamins and minerals to support overall health, reproductive performance, immune function, and egg quality. This may include vitamins A, D, E, B-complex vitamins, and minerals such as selenium, zinc, and manganese. Proper levels of vitamins and minerals are critical for maintaining optimal egg production, shell quality, and overall bird health.
- Additives: Some broiler layer feeds may contain additives such as probiotics, prebiotics, enzymes, or organic acids to promote gut health, nutrient utilization, and overall performance in laying hens. These additives can help improve feed efficiency, enhance nutrient absorption, and support digestive health, leading to better egg production and flock performance.